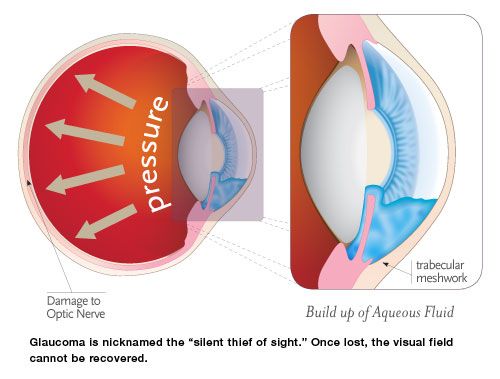
Tonometer tonometry is an optical technique used to measure the pressure of the fluid inside the eye. It is a non-invasive method of measuring intraocular pressure (IOP) and is used to diagnose glaucoma. Tonometry measures the resistance of the eye to pressure.
The equipment used to measure the pressure normally in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) are called tonometer’s and field of expertise tonometry. The tonometer is designed to detect changes in the pressure of the eye, and is used to help determine whether a person has glaucoma or is at risk of developing it. It can also help determine if any treatments are necessary to reduce the pressure in the eye. A common pressure reading should be around 15mmHg, and the range is usually around 10 mmHg to 20 mmHg. Where ordinary fluctuations are expected due to stress, drugs and health conditions extreme variations and a reading well above or below these can be an indication of underlining medical conditions.